ACME provides transnational access on the basis of scientific merit to a wide range of complementary astroparticle, high-energy and astronomical Research Infrastructures. This will open new opportunities for the science community in the detection, analysis and subsequent follow up of multi-messenger and high-energy time-domain astrophysical events.
The list below reports all the Research Infrastructures offering such transnational access (identified with the tag “TNA”), as well as other telescopes and detectors taking part in other ACME actions.
Radio
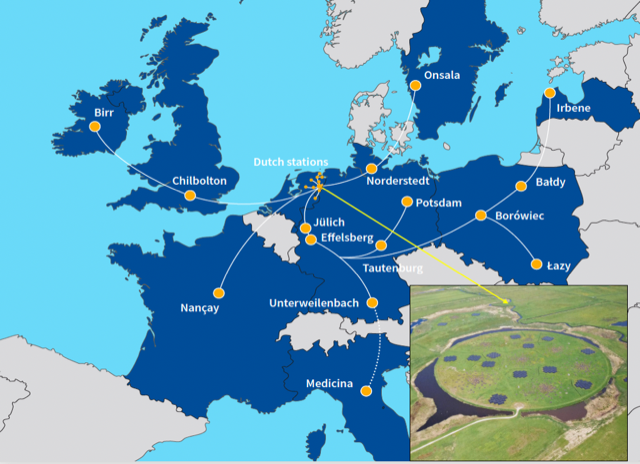
e-MERLIN
e-MERLIN is an array of seven radio telescopes spanning 217 km (135 miles) across Great Britain connected by a superfast optical fibre network to its headquarters at Jodrell Bank Observatory. It has a unique position in the world with an angular resolution comparable...
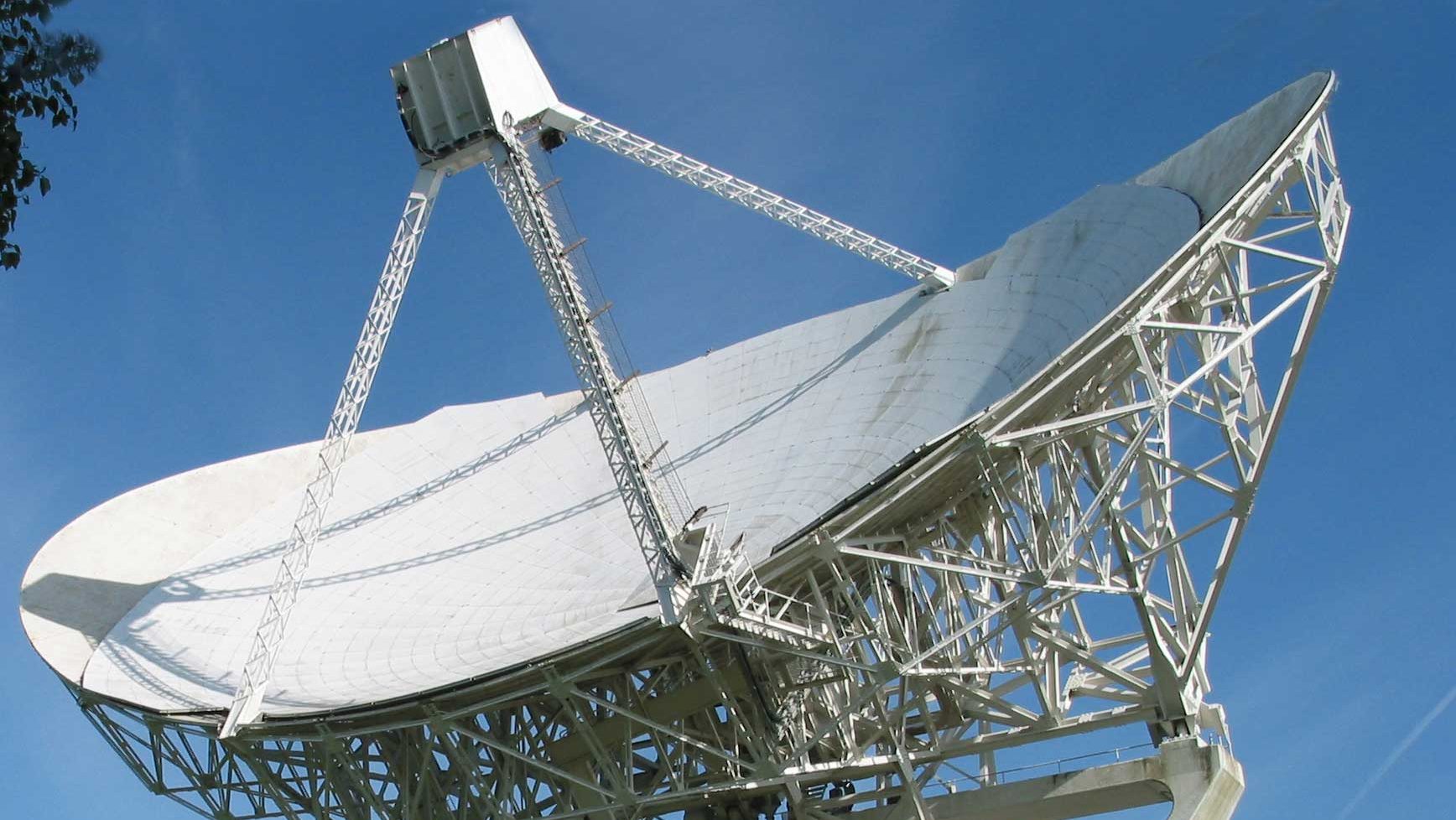
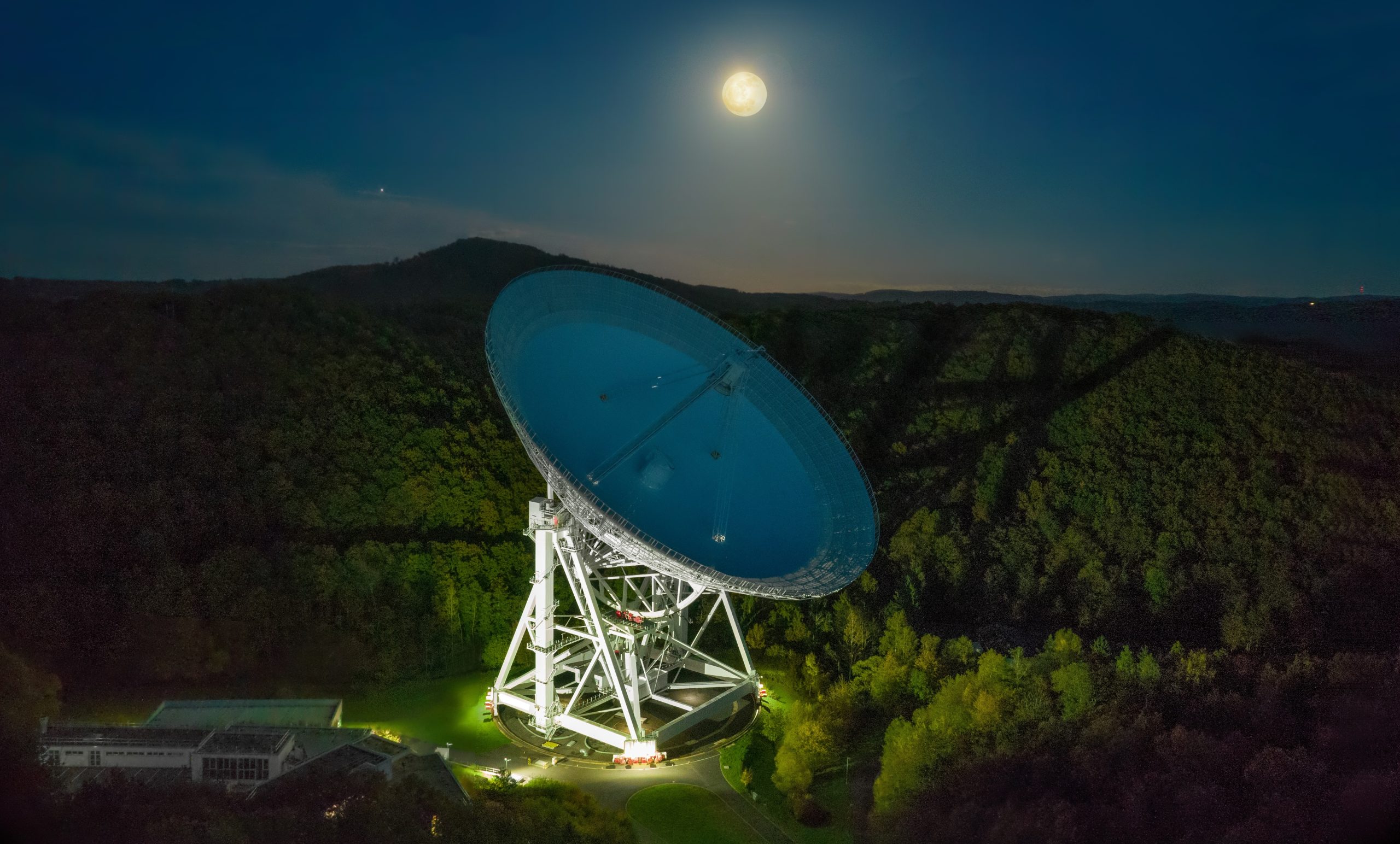
Effelsberg
Effelsberg 100m Radio Telescope The 100-m Radio Telescope of the Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie (MPIfR) is a unique European astronomical facility that combines superb sensitivity and wide frequency coverage (300 MHz to 90 GHz) with distinct versatility. The...
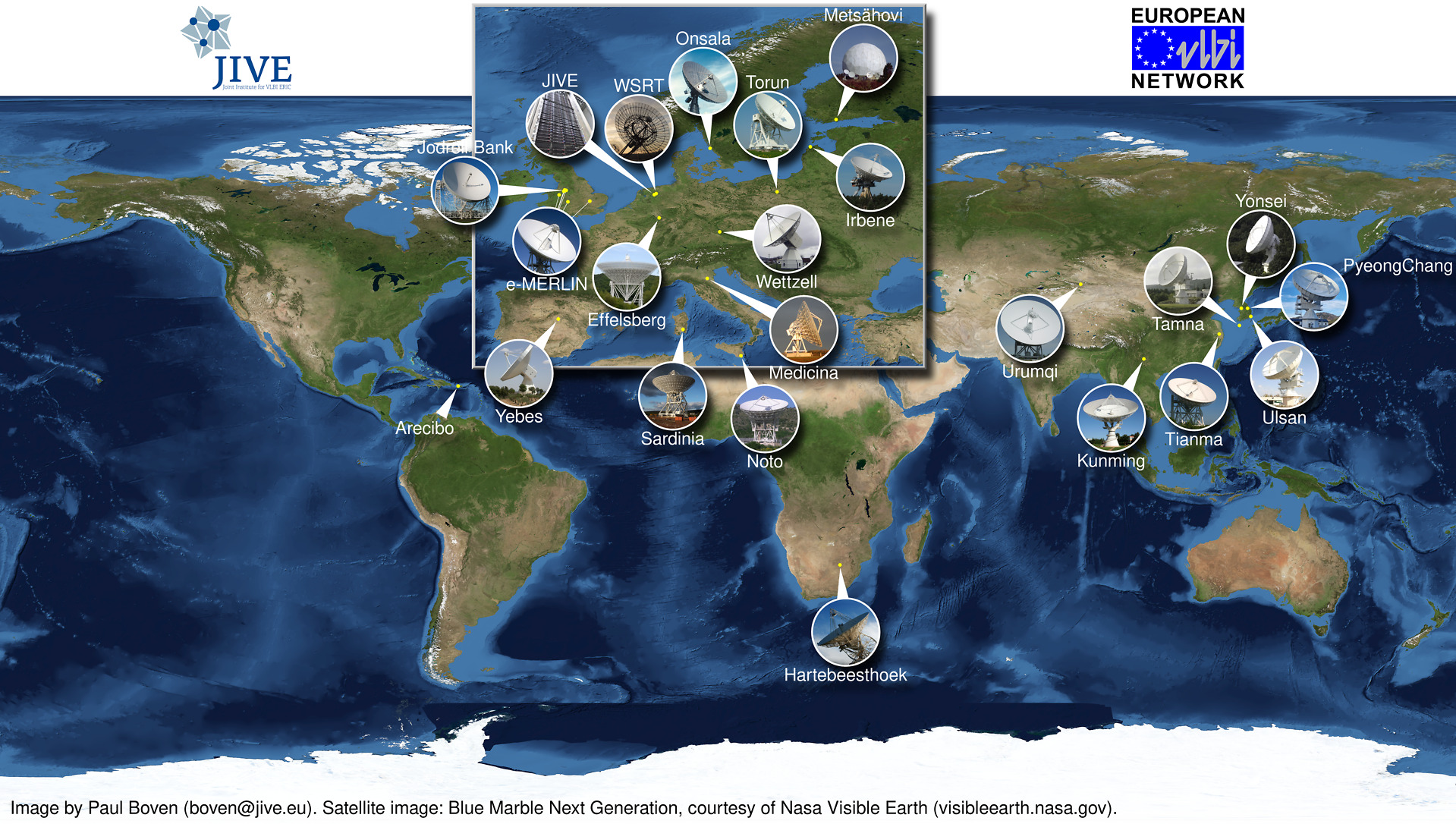
EVN
The European VLBI Network (EVN) is an interferometric array of twelve radio telescopes spread throughout Europe, but also including eight telescopes in Asia and South Africa. With baselines ranging from 260-10k km, it provides sub-milliarcsecond imaging and...
IRAM
NOEMA and the IRAM 30-meter telescopes are the world's most sensitive (sub-)mm astronomical facilities operating in the northern hemisphere. The 30m-telescope and NOEMA cover a broad range of science topics from the study of solar system comets to VLBI observations of...
LOFAR
The LOw Frequency ARray (LOFAR) is the world’s largest and most sensitive low-frequency radio telescope. It is a network of 52 geographically distributed antenna stations that stretches across Europe. With its versatility and its unique spectral coverage (10 - 250...
NenuFar
Located on the site of the Nançay Radio Observatory (200 km south of Paris) in France, NenuFAR is a very large low-frequency radio telescope, which is among the most powerful in the world in its frequency range between 10 MHz and 85 MHz. This range corresponds to the...
UTR-2
UTR-2 is the telescope in Ukraine that has pioneered astronomical observations at the lowest radio frequencies down to 10 MHz. Even though the telescope has been damaged by the russian troops during the russian invasion in 2022, its data archive has been preserved....
Optical
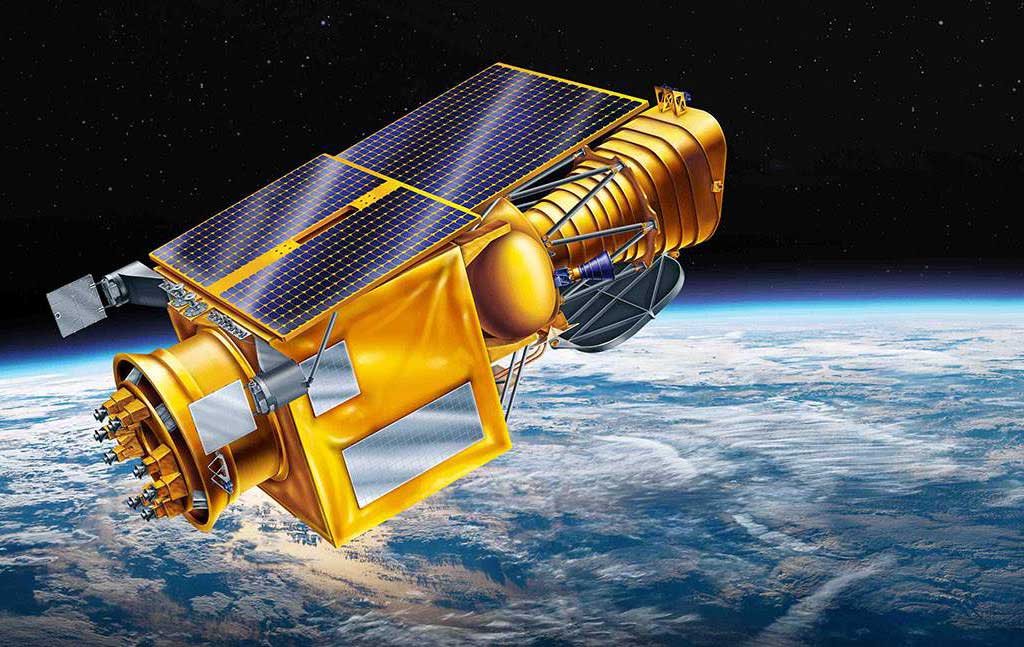
ULTRASAT
ULTRASAT is a scientific satellite that is planned to be launched to GEO orbit in Q2 2026. It will be carrying a telescope with an unprecedentedly large field of view (204 squared degrees), that will conduct the first wide-field survey of transient and variable...
BHTOM
BHTOM is a cutting-edge research infrastructure, part of the ACME grant, revolutionising time-domain astronomy. It connects a global network of over 120 optical telescopes—ranging from 0.25 to 2.5 meters in aperture—including professional facilities, amateur setups,...
CFHT
CFHT is a 3.6-m diameter telescope located at the summit of Mauna Kea, a 4200-m high dormant volcano in Hawai’i. CFHT operates 100% in service observing mode and provides pre- processed data to its users. Its unique location with full coverage of the Northern Sky and...
Neutrinos & Cosmic rays
IceCube
The IceCube Collaboration is operating the world's most sensitive high-energy neutrino detector. Deployed between 1.5 and 2.5 km depth in the Antarctic glacier ice at the South Pole, the detector is taking data with an uptime of >99%, monitoring the full neutrino...
ANTARES
ANTARES was a neutrino detector located 2.5 km deep in the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Toulon (France). It has operated from 2008 to 2022 and produced many results on the search for a cosmic diffuse neutrino flux, the search for steady neutrino sources in the...
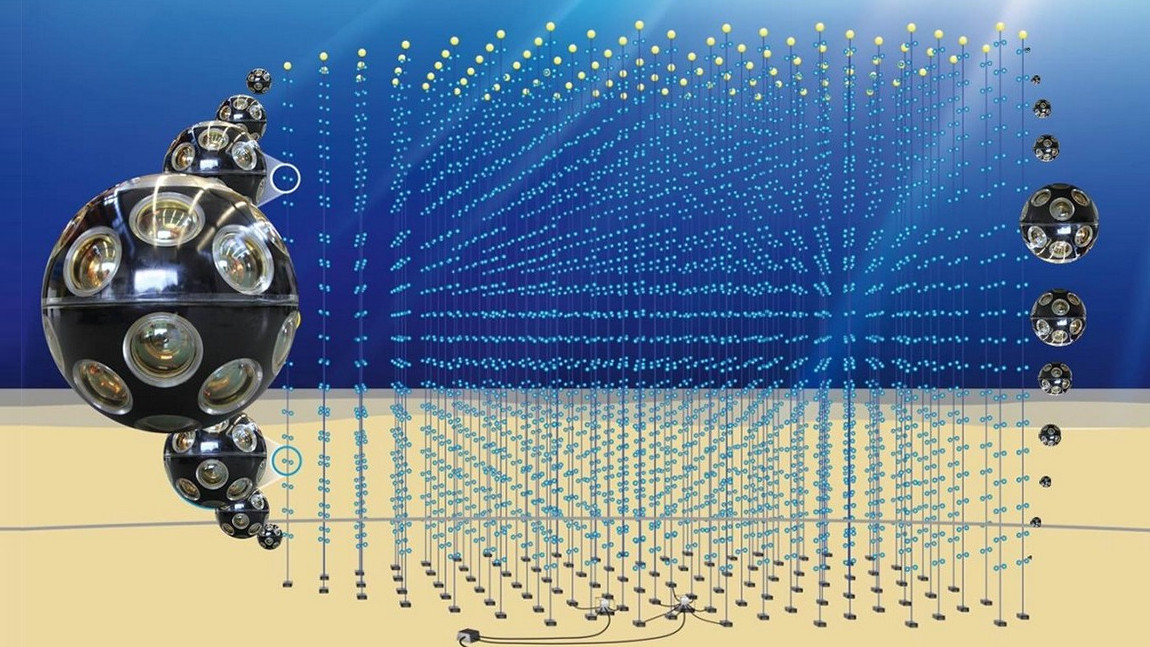
KM3NeT
The Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope or KM3NeT is a research infrastructure located at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea, mainly aiming for the detection of neutrinos. It employs the detection of Cherenkov light to identify and reconstruct the direction of...
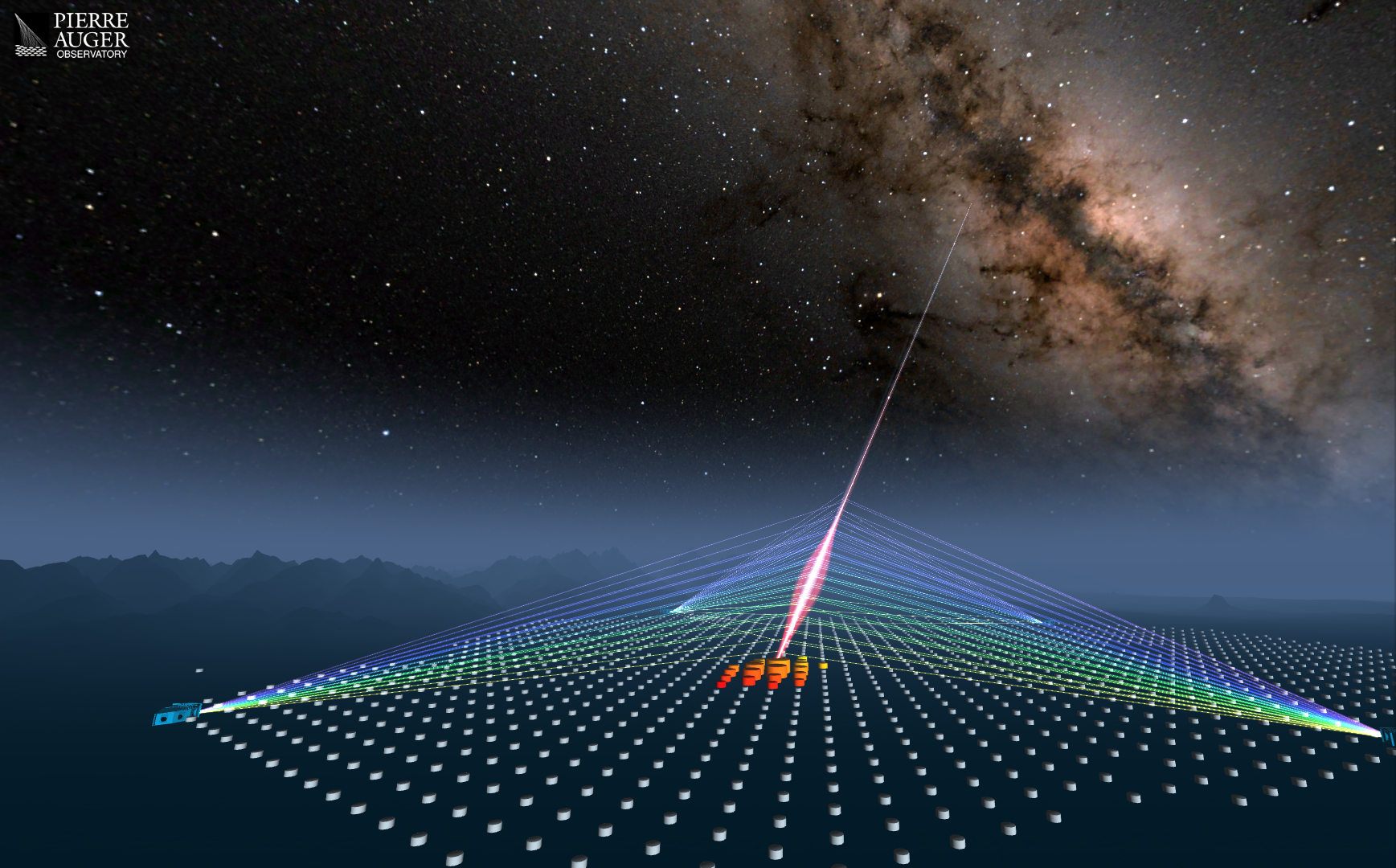
Pierre Auger Observatory
The Observatory and its recent upgrade, AugerPrime, is the largest, most complete and precise detector of giant air showers of energy exceeding 100 PeV. It is a multi-hybrid Observatory consisting of a large array of 1600 detector stations 1500 m apart, in Mendoza...
Gamma Rays
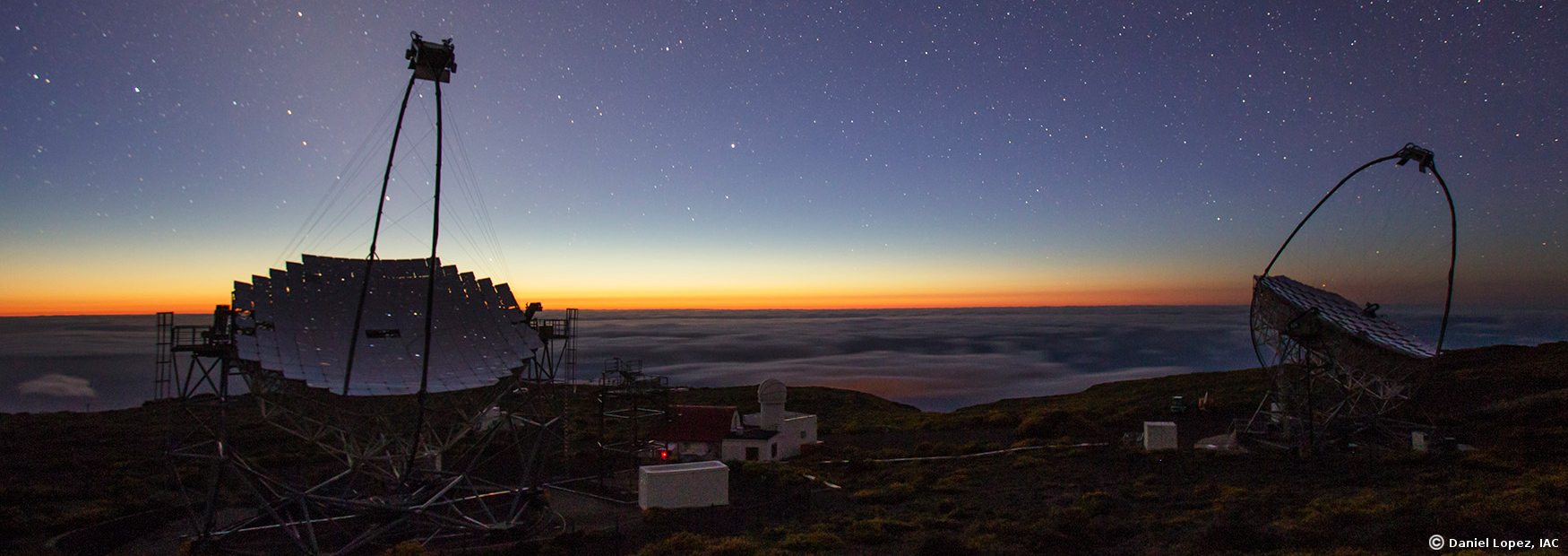
MAGIC
TNA Call: The submission deadline is January 23, 2026 at 23:59 UT. For all the details, see: https://magic.mpp.mpg.de/public/magicop/ Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov (MAGIC) is a system of two 17 m diameter Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes...
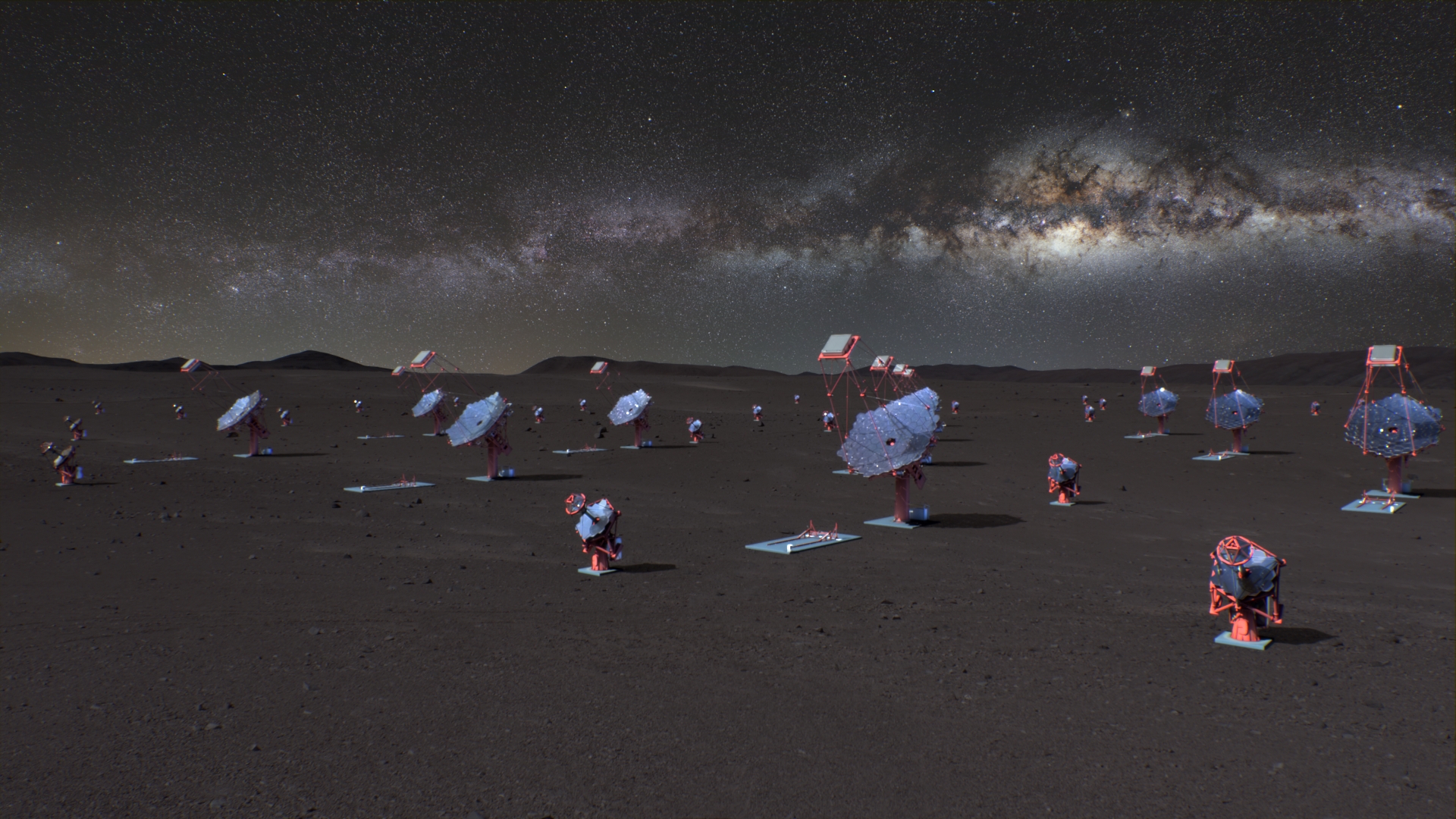
CTAO
The Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO) is the next-generation facility for ground-based very-high-energy gamma-ray astronomy. It is overseen by the CTAO ERIC legal entity established in January 2025. This date marks the official start of the project...
Gravitational waves
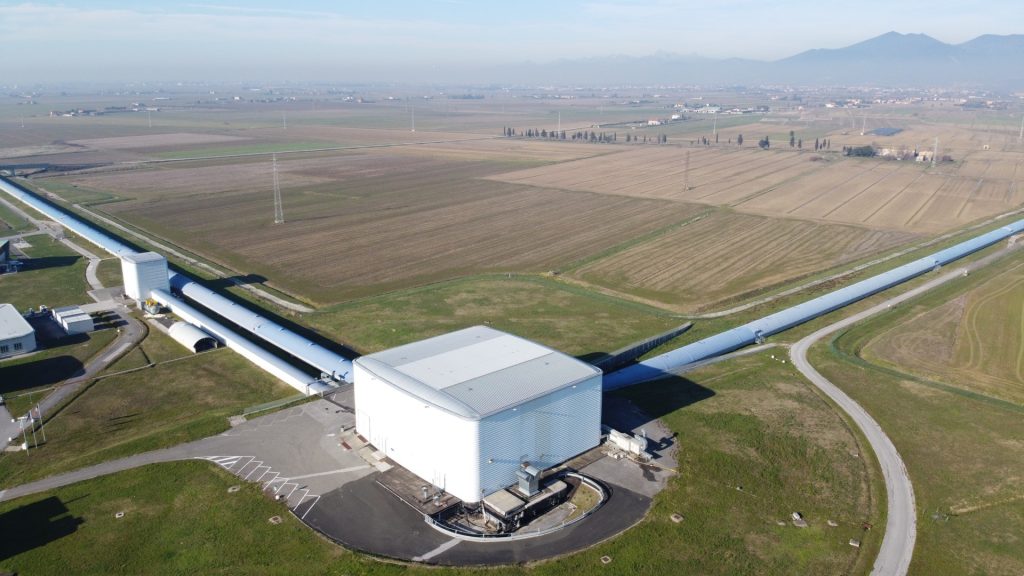
Virgo
Virgo is a gravitational-wave detector and laser interferometer, featuring two 3-kilometer-long arms arranged in an L-shape. It is sensitive to gravitational waves in the 10 Hz to 5 kHz frequency band, enabling it to observe astrophysical events such as the...